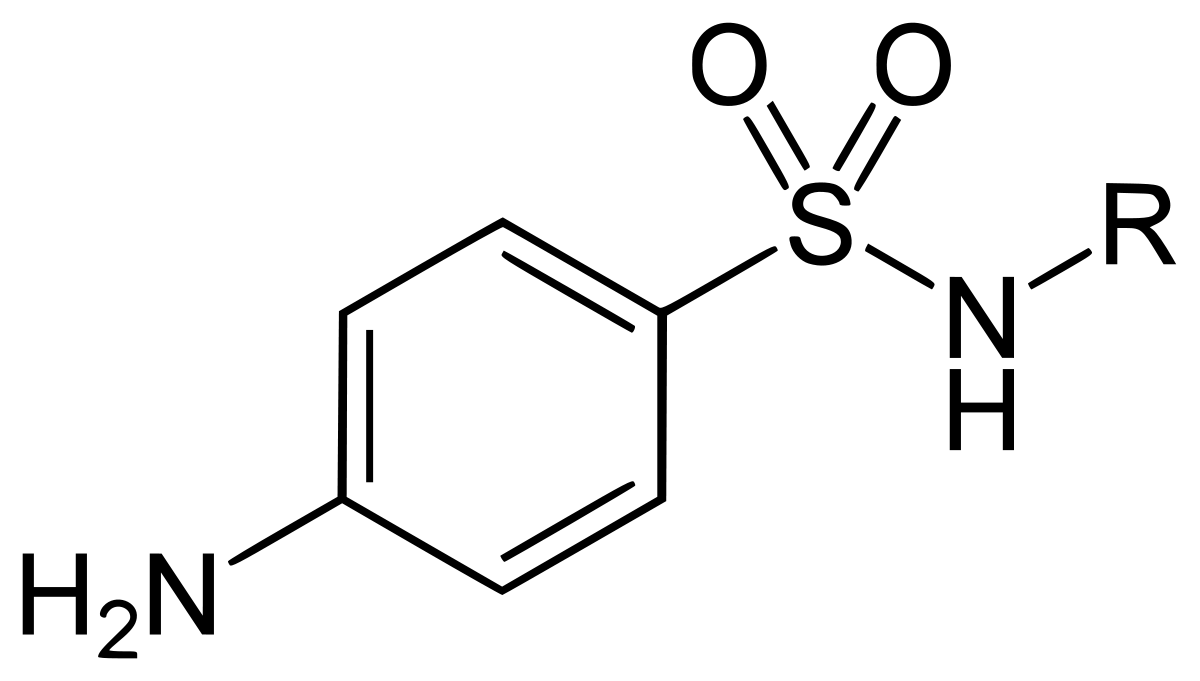
Sulfonamides have the advantages of broad antibacterial spectrum, stable properties, low price and a variety of preparations to choose from. The basic structure of sulfonamides is p-sulfanilamide. It can interfere with the synthesis of bacterial folic acid and affect its growth and reproduction, thereby inhibiting most Gram-positive bacteria and some negative bacteria.
Bacteria that are highly sensitive to sulfa include: Streptococcus, Pneumococcus, Salmonella, etc., and moderately sensitive are: Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Pasteurella, Shigella, Listeria, some Actinomyces and Treponema hyodysenteriae Also sensitive to sulfonamides; also effective against certain protozoa such as coccidia. Bacteria sensitive to sulfonamides can develop resistance.
In actual use, sulfonamides are often used in conjunction with other drugs. Most of the adverse effects of long-term use of early sulfonamides are urinary tract disturbances, renal impairment and reduced feed intake.
In order to reduce its toxic and side effects, first, the dosage should be appropriate, and it should not be increased or decreased at will. If the dosage is too large, it will increase the toxic and side effects, and if the dosage is too small, it will not only have no therapeutic effect, but will cause the pathogenic bacteria to develop drug resistance. Second, use with other drugs, such as amproline and sulfonamide synergists, to reduce the dosage. Third, if the formula allows, an equal amount of sodium bicarbonate can be added. Fourth, bacteria can produce different degrees of cross-resistance to sulfa drugs, so when they are resistant to a certain sulfa drug, it is not suitable to switch to another sulfa drug. Generally speaking, the initial dose of sulfa drugs must be doubled, and after the acute period, the drug should be insisted on taking it for 3-4 days before it can be stopped.
Post time: May-25-2022