Frozen Earth – White Earth
01 The Color of Life Planet
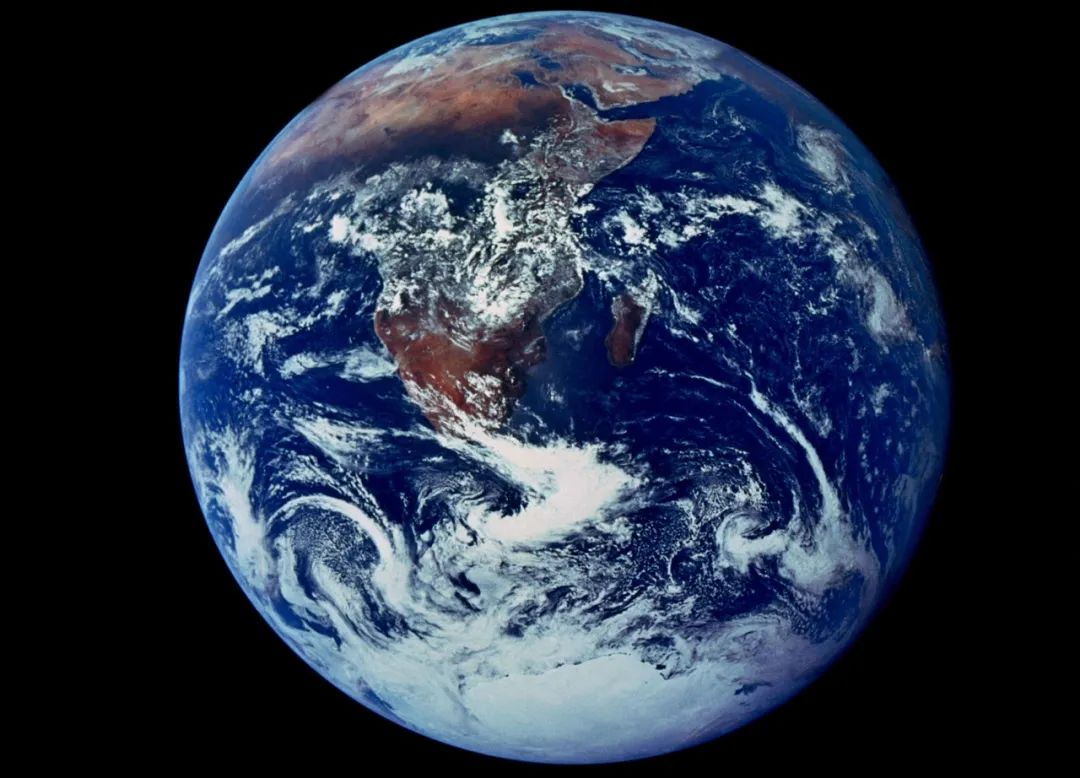
With more and more satellites or space stations flying in space, more and more photos of the Earth are being sent back. We often describe ourselves as a blue planet because 70% of the Earth’s area is covered by oceans. As the Earth warms, the melting rate of glaciers in the North and South Poles accelerates, and sea levels will continue to rise, eroding existing land. In the future, the ocean area will become larger, and the Earth’s climate will become increasingly complex. This year is very hot, next year is very cold, the year before last is very dry, and the year after next rainstorm is disastrous. We all say that the earth is almost unfit for human habitation, but in fact, this is just a small normal change of the earth. In the face of the powerful laws and forces of nature, human beings are nothing.
With more and more satellites or space stations flying in space, more and more photos of the Earth are being sent back. We often describe ourselves as a blue planet because 70% of the Earth’s area is covered by oceans. As the Earth warms, the melting rate of glaciers in the North and South Poles accelerates, and sea levels will continue to rise, eroding existing land. In the future, the ocean area will become larger, and the Earth’s climate will become increasingly complex. This year is very hot, next year is very cold, the year before last is very dry, and the year after next rainstorm is disastrous. We all say that the earth is almost unfit for human habitation, but in fact, this is just a small normal change of the earth. In the face of the powerful laws and forces of nature, human beings are nothing.
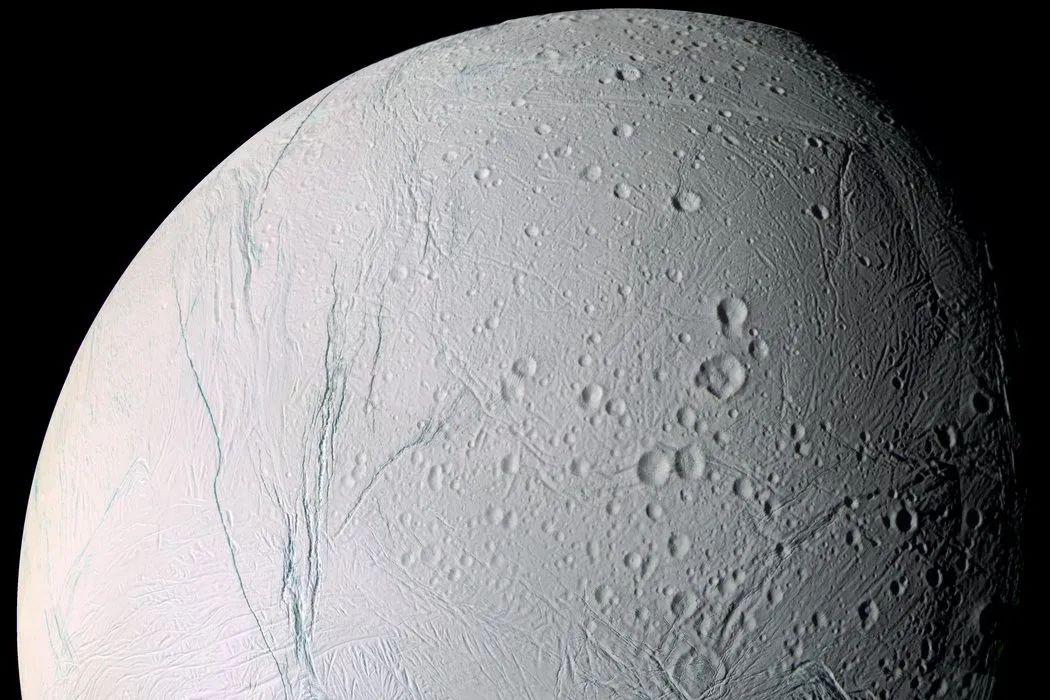
In 1992, Joseph Kirschvink, a professor of geology at the California Institute of Technology, first used the term “Snowball Earth”, which was later supported and improved by major geologists. Snowball Earth is a hypothesis that cannot be fully determined at present, used to describe the largest and most severe ice age in Earth’s history. The Earth’s climate was extremely complex, with an average global temperature of -40-50 degrees Celsius, to the point where the Earth was so cold that the surface only had ice.
02 The Ice Cover of Snowball Earth
Snowball Earth probably occurred in the Neoproterozoic (approximately 1-6 billion years ago), belonging to the Proterozoic period of the Precambrian. The history of the Earth is very ancient and long. It was said before that the millions of years of human history is just a blink of an eye for the Earth. We often think that the current Earth is so special under human transformation, but in fact, it is nothing to the history of the Earth and life. The Mesozoic, Archean, and Proterozoic eras (collectively known as the Cryptozoic eras, which occupy approximately 4 billion years of Earth’s 4.6 billion years), and the Ediacaran period in the Neoproterozoic era of the Proterozoic era is a special period of life on Earth.
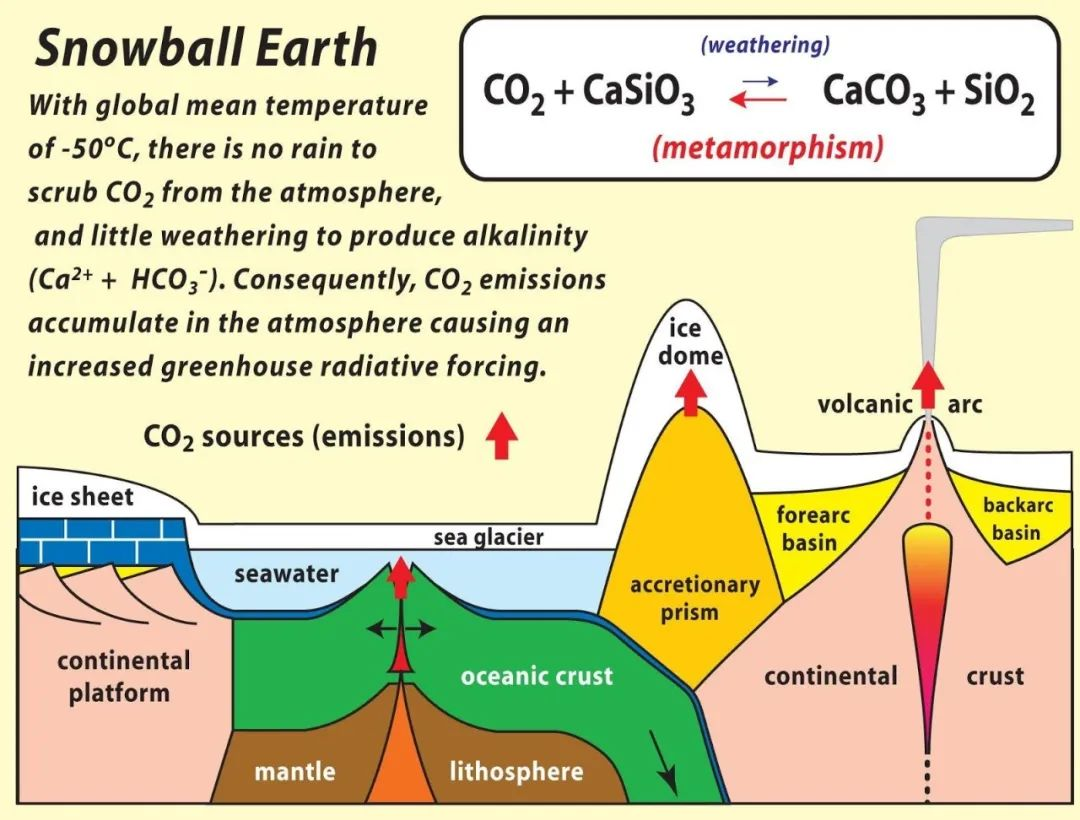
During the Snowball Earth period, the ground was completely covered with snow and ice, with no oceans or land. At the beginning of this period, there was only one piece of land on Earth called the supercontinent (Rodinia) near the equator, and the rest of the area was oceans. When the Earth is in an active state, volcanoes continue to erupt, more rocks and islands appear on the sea surface, and the land area continues to expand. The carbon dioxide emitted by volcanoes envelops the Earth, forming a greenhouse effect. Glaciers, like now, are concentrated at the north and south poles of the Earth, unable to cover land near the equator. As Earth activity stabilizes, volcanic eruptions also begin to decrease, and the amount of carbon dioxide in the air also begins to decrease. The important contributor to absorbing carbon dioxide is rock weathering. According to the classification of mineral composition, rocks are mainly divided into silicate rocks and carbonate rocks. Silicate rocks absorb atmospheric CO2 during chemical weathering, and then store CO2 in the form of CaCO3, forming a geological time scale carbon sink effect (>1 million years). Carbonate rock weathering can also absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, forming a shorter time scale carbon sink (<100000 years) in the form of HCO3-.
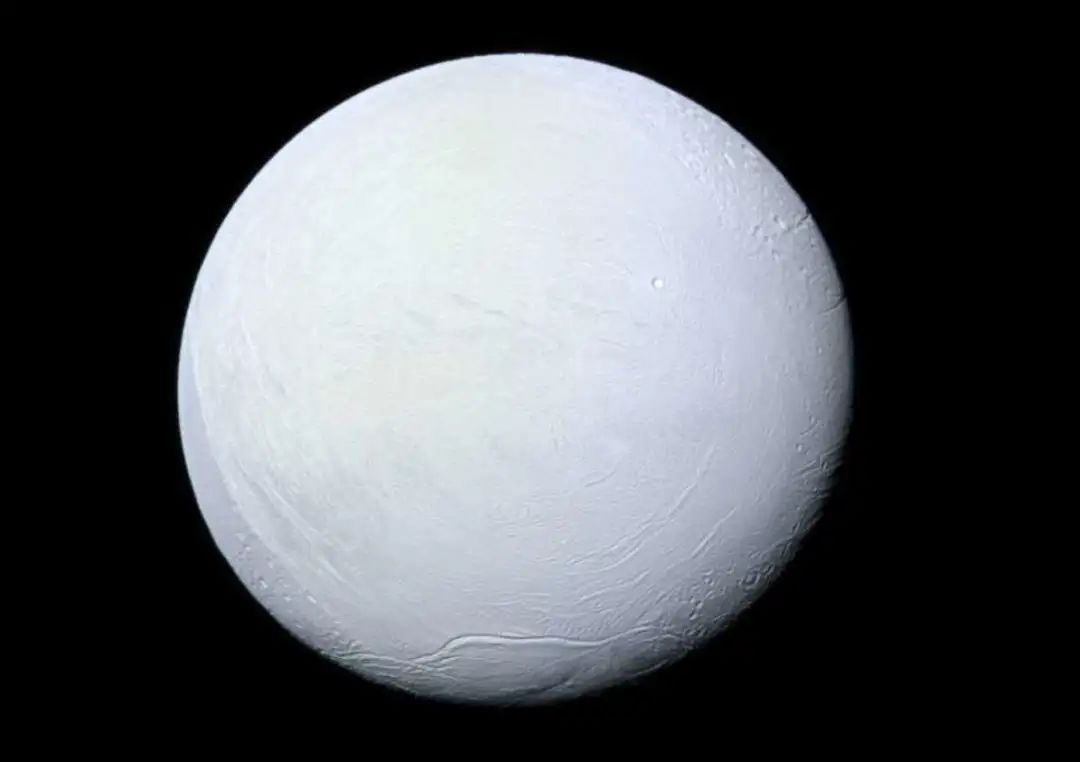
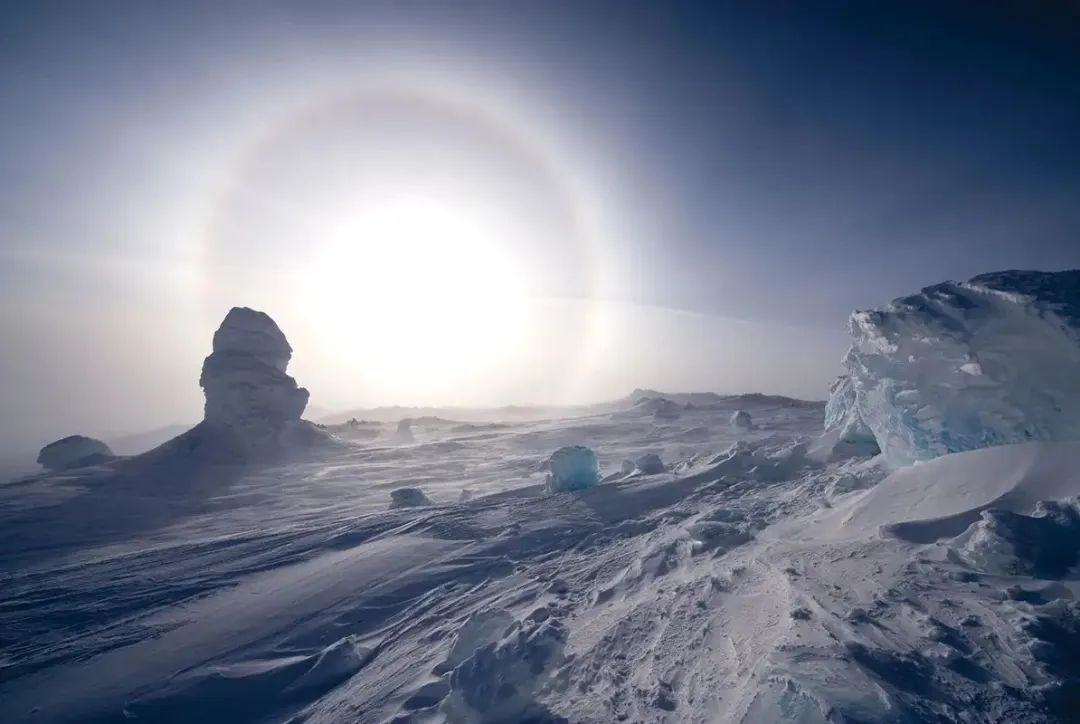
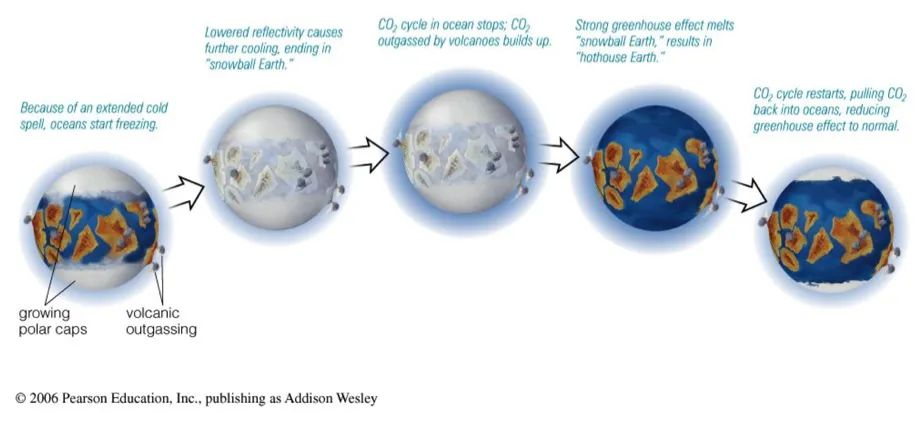
This is a dynamic equilibrium process. When the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by rock weathering exceeds the amount of volcanic emissions, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere begins to rapidly decrease, until greenhouse gases are completely consumed and temperatures begin to drop. Glaciers at the two poles of the Earth begin to spread freely. As the area of glaciers increases, there are more and more white areas on the Earth’s surface, and sunlight is reflected back into space by the snowy Earth, Further exacerbating the temperature drop and accelerating the formation of glaciers. The number of cooling glaciers increases – more sunlight reflects – further cooling – more white glaciers. In this cycle, the glaciers at both poles gradually freeze all the oceans, eventually healing on the continents near the equator, and finally forming a huge ice sheet with a thickness of over 3000 meters, wrapping the Earth completely into a ball of ice and snow. At this time, the uplift effect of water vapor on the Earth was significantly reduced, and the air was exceptionally dry. Sunlight shone on the Earth without fear, and was then reflected back. The intensity of ultraviolet radiation and the cold temperature made it impossible for any life to exist on the Earth’s surface. Scientists refer to the Earth over billions of years as’ White Earth ‘or’ Snowball Earth ‘
03 The Melting of Snowball Earth
Last month, when I talked to my friends about the Earth during this period, someone asked me, ‘According to this cycle, the Earth should always be frozen. How did it melt later?’? This is the great law of nature and the power of self repair.
As the Earth is completely covered by ice up to 3000 meters thick, rocks and air are isolated, and rocks cannot absorb carbon dioxide through weathering. However, the activity of the Earth itself can still lead to volcanic eruptions, slowly releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. According to scientists’ calculations, if we want the ice on Snowball Earth to dissolve, the concentration of carbon dioxide needs to be approximately 350 times the current concentration on Earth, accounting for over 13% of the entire atmosphere (now 0.03%), and this increase process is very slow. It took about 30 million years for the Earth’s atmosphere to accumulate enough carbon dioxide and methane, forming a strong greenhouse effect. Glaciers began to melt, and the continents near the equator began to expose ice. The exposed ground was darker in color than the ice, absorbing more solar heat and initiating a positive feedback. The Earth’s temperature further increased, glaciers further decreased, reflecting less sunlight, and exposing more rocks, Absorbing more heat, gradually forming non freezing rivers… and the Earth begins to recover!
Last month, when I talked to my friends about the Earth during this period, someone asked me, ‘According to this cycle, the Earth should always be frozen. How did it melt later?’? This is the great law of nature and the power of self repair.
As the Earth is completely covered by ice up to 3000 meters thick, rocks and air are isolated, and rocks cannot absorb carbon dioxide through weathering. However, the activity of the Earth itself can still lead to volcanic eruptions, slowly releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. According to scientists’ calculations, if we want the ice on Snowball Earth to dissolve, the concentration of carbon dioxide needs to be approximately 350 times the current concentration on Earth, accounting for over 13% of the entire atmosphere (now 0.03%), and this increase process is very slow. It took about 30 million years for the Earth’s atmosphere to accumulate enough carbon dioxide and methane, forming a strong greenhouse effect. Glaciers began to melt, and the continents near the equator began to expose ice. The exposed ground was darker in color than the ice, absorbing more solar heat and initiating a positive feedback. The Earth’s temperature further increased, glaciers further decreased, reflecting less sunlight, and exposing more rocks, Absorbing more heat, gradually forming non freezing rivers… and the Earth begins to recover!
The complexity of natural laws and Earth’s ecology far exceeds our human understanding and imagination. The increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration leads to global warming, and higher temperatures enhance the chemical weathering of rocks. The amount of CO2 absorbed from the atmosphere also increases, thereby suppressing the rapid growth of atmospheric CO2 and leading to global cooling, forming a negative feedback mechanism. On the other hand, when the Earth’s temperature is low, the intensity of chemical weathering is also at a lower level, and the flux of absorbing atmospheric CO2 is very limited. As a result, the CO2 emitted by volcanic activities and rock metamorphism can accumulate, promoting the development of the Earth towards warming and preventing the Earth’s temperature from being too low.
This change, which is often measured in billions of years, is not something that human beings can control. As ordinary members of nature, what we should do more is to adapt to nature and conform to its laws, rather than changing or destroying nature. Protecting the environment and loving life is what every human being should do, otherwise we will only face extinction.
Post time: Aug-29-2023